Abstract
Acquired hemophilia A (AHA) is a rare autoimmune disorder caused by the development of autoantibodies against the factor (F)VIII of coagulation with higher incidence in elderly individuals. The treatment includes immunosuppressive alternatives, and the majority of patients reach complete remission of symptoms. Although the role of immune T and B cells in the physiopathology of several autoimmune diseases is widely established, few studies have explored the T and B cells immune response pathway in AHA. This study aimed to determine the role of T cells through their cytokines expression and B cells through their expression of proteins that activate the B cell receptor (BCR), such as B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and A-proliferation inducing ligand (APRIL), in a longitudinal evaluation of patients with AHA.
We included in this study 11 patients, 4 (36%) male, with the diagnosis of AHA, based on the occurrence of low FVIII levels (median FVIII level at the diagnosis was 0.10 IU/dL; range 0-18.8) and anti-FVIII inhibitor titer positive (≥0.6 Bethesda units (BU)/mL) (median inhibitor titer at the diagnosis was 60BU/mL; range 7.6-1000.2). The median age at the diagnosis was 59 years (range 9-75). Idiopathic AHA was evident in 72.7% of cases, while autoimmune diseases (18.2%), and pregnancy (9.1%) were the other underlying etiologies. All patients received immunosuppressive therapy (IST). Eight (72.7%) patients used corticosteroid (CS) plus cyclophosphamide (CP), one (9.1%) received only CP, one (9.1%) used CS plus rituximab and one (9.1%) received CS, CP and three cycles of rituximab. The response to IST was defined as complete remission (CR) with anti-FVIII < 0.6BU/mL and FVIII >50IU/dL, without further IST. Relapse was defined when anti-FVIII titer became >0.6BU/mL after previous remission. In this cohort, we observed 64% of sustained CR and 4(36%) AHA patients had at least one relapse, including two AHA patients considered idiopathic and two with other autoimmune diseases associated.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were collected from all AHA patients at the diagnosis previously IST (baseline), when patient achieved CR, and at the occurrence of relapse. PBMCs were maintaining frozen in liquid nitrogen. Cells were taw and cultivated with RMPI-1640 medium in 7.5x10 5 cells/well in a 48-well plate. After 24h, cells were stimulated with a 1IU/well of a full-length recombinant FVIII concentrate (rFVIII) or phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) (1µM) with ionomycin (1µM). After 24h incubation, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry at BD FACSCalibur™.
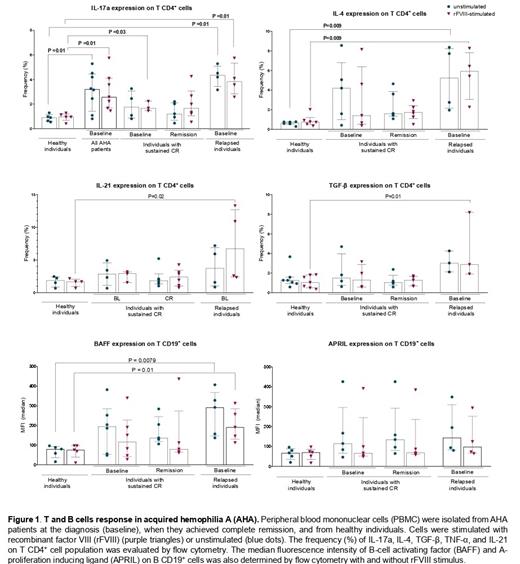
To determine T CD4 + cells' cytokine production profile, we stained T cells with anti-CD4, anti-interleukins (IL)-17a, IL-4, and IL-21, anti-TGF-b, and anti-TNF-a. We observed a significant increase of IL-17a production in the rFVIII-stimulated cells isolated at baseline from all patients compared to cells isolated from healthy individuals (P=0.01). However, IL-17a expression at baseline was not different between cells from patients who sustained CR to those who relapsed. Interestingly, when we compared cells isolated at baseline from patients that relapsed after different immunosuppressive attempts, we observed a significant difference for IL-4 (P=0.009), IL-21 (P=0.02), and TGF-b (P=0.01) expression in comparison to cells from healthy individuals. However, this difference was not observed in cells from sustained CR vs. cells from healthy individuals (figure 1). Thus, suggesting that all patients present Th17 response, while only patients that relapsed also showed Th2 response at the diagnosis.
We also evaluated B cells' expression of BAFF and APRIL. The cells were stained with anti-CD19, BAFF, and APRIL. Only cells isolated at baseline from AHA relapsed patients after rFVIII stimulation or without any stimuli presented increased expression of BAFF (P=0.01 with rFVIII-stimulated and P=0.007 for unstimulated cells) when compared to PBMCs isolated from healthy individuals (figure 1). BAFF is responsible for controlling B-cell maturation and is associated with autoantibody production of different autoimmune conditions.
Our finds reveal an increase in the Th17 response in patients with AHA at the diagnosis. However, the presence of Th2 response and increase of BAFF expression was observed only at the diagnosis of patients with recurrence of autoimmune response to FVIII, which suggests a potential biomarker for AHA evaluation.
Ozelo: BioMarin: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bayer: Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Grifols: Other: Grant review.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal